Archive for the ‘Seeing Things As They Are’ Category
What it Takes to Do New Work
What it takes to do new work.
Confidence to get it wrong and confidence to do it early and often.
Purposeful misuse of worst practices in a way that makes them the right practices.
Tolerance for not knowing what to do next and tolerance for those uncomfortable with that.
Certainty that they’ll ask for a hard completion date and certainty you won’t hit it.
Knowledge that the context is different and knowledge that everyone still wants to behave like it’s not.
Disdain for best practices.
Discomfort with success because it creates discomfort when it’s time for new work.
Certainty you’ll miss the mark and certainty you’ll laugh about it next week.
Trust in others’ bias to do what worked last time and trust that it’s a recipe for disaster.
Belief that successful business models have half-lives and belief that no one else does.
Trust that others will think nothing will come of the work and trust that they’re likely right.
Image credit — japanexpertna.se
28 Things I Learned the Hard Way
- If you want to have an IoT (Internet of Things) program, you’ve got to connect your products.
- If you want to build trust, give without getting.
- If you need someone with experience in manufacturing automation, hire a pro.
- If the engineering team wants to spend a year playing with a new technology, before the bell rings for recess ask them what solution they’ll provide and then go ask customers how much they’ll pay and how many they’ll buy.
- If you don’t have the resources, you don’t have a project.
- If you know how it will turn out, let someone else do it.
- If you want to make a friend, help them.
- If your products are not connected, you may think you have an IoT program, but you have something else.
- If you don’t have trust, you have just what you earned.
- If you hire a pro in manufacturing automation, listen to them.
- If Marketing has an optimistic sales forecast for the yet-to-be-launched product, go ask customers how much they’ll pay and how many they’ll buy.
- If you don’t have a project manager, you don’t have a project.
- If you know how it will turn out, teach someone else how to do it.
- If a friend needs help, help them.
- If you want to connect your products at a rate faster than you sell them, connect the products you’ve already sold.
- If you haven’t started building trust, you started too late.
- If you want to pull in the delivery date for your new manufacturing automation, instead, tell your customers you’ve pushed out the launch date.
- If the VP knows it’s a great idea, go ask customers how much they’ll pay and how many they’ll buy.
- If you can’t commercialize, you don’t have a project.
- If you know how it will turn out, do something else.
- If a friend asks you twice for help, drop what you’re doing and help them immediately.
- If you can’t figure out how to make money with IoT, it’s because you’re focusing on how to make money at the expense of delivering value to customers.
- If you don’t have trust, you don’t have much
- If you don’t like extreme lead times and exorbitant capital costs, manufacturing automation is not for you.
- If the management team doesn’t like the idea, go ask customers how much they’ll pay and how many they’ll buy.
- If you’re not willing to finish a project, you shouldn’t be willing to start.
- If you know how it will turn out, it’s not innovation.
- If you see a friend that needs help, help them ask you for help.
Image credit — openDemocracy
Use less, make more.
 If you use fewer natural resources, your product costs less.
If you use fewer natural resources, your product costs less.
If you use recycled materials, your product costs less.
If you use less electricity, your product costs less.
If you use less water to make your product, your product costs less.
If you use less fuel to ship your product, your product costs less.
If you make your product lighter, your product costs less.
If you use less packaging, your product costs less.
If you don’t want to be environmentally responsible because you think it’s right, at least do it to be more profitable.
Image credit — Sandrine Néel
The Five Hardships of Success
 Everything has a half-life, but we don’t behave that way. Especially when it comes to success. The thinking goes – if it was successful last time, it will be successful next time. So, do it again. And again. It’s an efficient strategy – the heavy resources to bring it to life have already been spent. And it’s predictable – the same customers, the same value proposition, the same supply base, the same distribution channel, and the same technology. And it’s dangerous.
Everything has a half-life, but we don’t behave that way. Especially when it comes to success. The thinking goes – if it was successful last time, it will be successful next time. So, do it again. And again. It’s an efficient strategy – the heavy resources to bring it to life have already been spent. And it’s predictable – the same customers, the same value proposition, the same supply base, the same distribution channel, and the same technology. And it’s dangerous.
Success is successful right up until it isn’t. It will go away. But it will take time. A successful product line won’t fall off the face of the earth overnight. It will deliver profits year-over-year and your company will come to expect them. And your company will get hooked on the lifestyle enabled by those profits. And because of the addiction, when they start to drop off the company will do whatever it takes to convince itself all is well. No need to change. If anything, it’s time to double-down on the successful formula.
Here’s a rule: When your successful recipe no longer brings success, it’s not time to double-down.
Success’s decline will be slow, so you have time. But creating a new recipe takes a long time, so it’s time to declare that the decline has already started. And it’s time to learn how to start work on the new recipe.
Hardship 1 – Allocate resources differently. The whole company wants to spend resources on the same old recipes, even when told not to. It’s time to create a funding stream that’s independent of the normal yearly planning cycle. Simply put, the people at the top have to reallocate a part of the operating budget to projects that will create the next successful platform.
Hardship 2 – Work differently. The company is used to polishing the old products and they don’t know how to create new ones. You need to hire someone who can partner with outside companies (likely startups), build internal teams with a healthy disrespect for previous success, create mechanisms to support those teams and teach them how to work in domains of high uncertainty.
Hardship 3 – See value differently. How do you provide value today? How will you provide value when you can’t do it that way? What is your business model? Are you sure that’s your business model? Which elements of your business model are immature? Are you sure? What is the next logical evolution of how you go about your business? Hire someone to help you answer those questions and create projects to bring the solutions to life.
Hardship 4 – Measure differently. When there’s no customer, no technology and no product, there’s no revenue. You’ve got to learn how to measure the value of the work (and the progress) with something other than revenue. Good luck with that.
Hardship 5 – Compensate differently. People that create something from nothing want different compensation than people that do continuous improvement. And you want to move quickly, violate the status quo, push through constraints and create whole new markets. Figure out the compensation schemes that give them what they want and helps them deliver what you want.
This work is hard, but it’s not impossible. But your company doesn’t have all the pieces to make it happen. Don’t be afraid to look outside your company for help and partnership.
Image credit — Insider Monkey
Where is petroleum consumed?
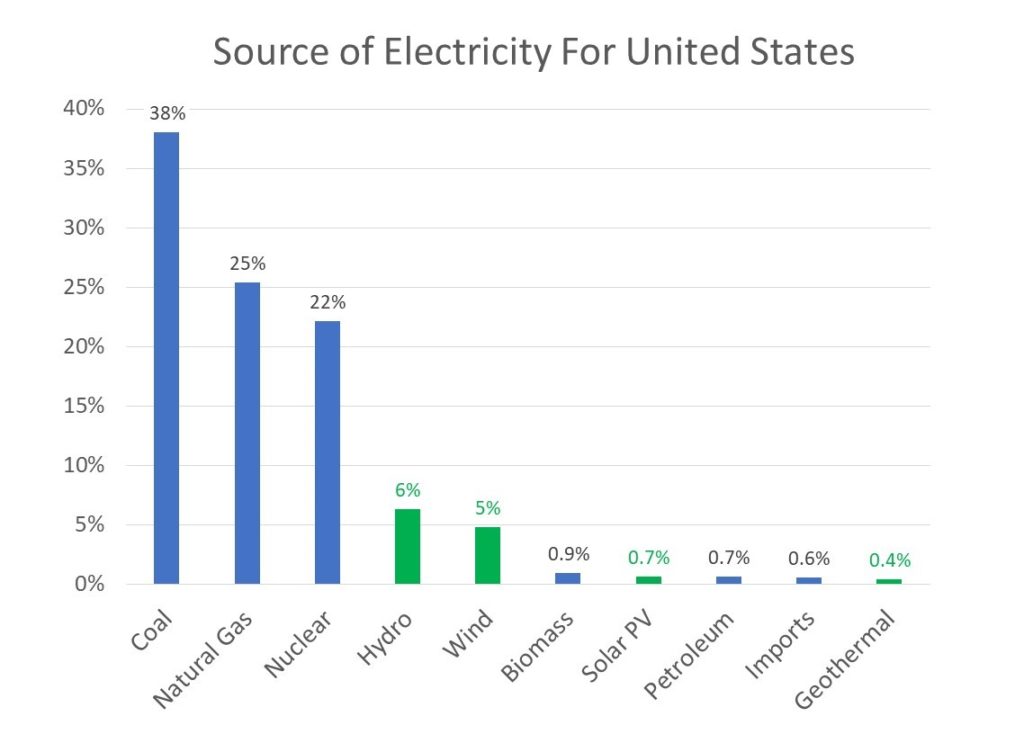
 In last week’s post, I provided a chart that describes the sources of electricity for the United States. Coal is the largest source of electricity (38%) and natural gas is the next largest (25%). The largest non-carbon source is nuclear (22%) and the largest renewable sources are wind (6%) and solar (5%). The data from the chart came from Otherlab who was contracted by the Advanced Research Project Agency of the Department of Energy (ARPA-e) to review all available energy data sources and create an ultra-high resolution picture of the U.S. energy economy.
In last week’s post, I provided a chart that describes the sources of electricity for the United States. Coal is the largest source of electricity (38%) and natural gas is the next largest (25%). The largest non-carbon source is nuclear (22%) and the largest renewable sources are wind (6%) and solar (5%). The data from the chart came from Otherlab who was contracted by the Advanced Research Project Agency of the Department of Energy (ARPA-e) to review all available energy data sources and create an ultra-high resolution picture of the U.S. energy economy.
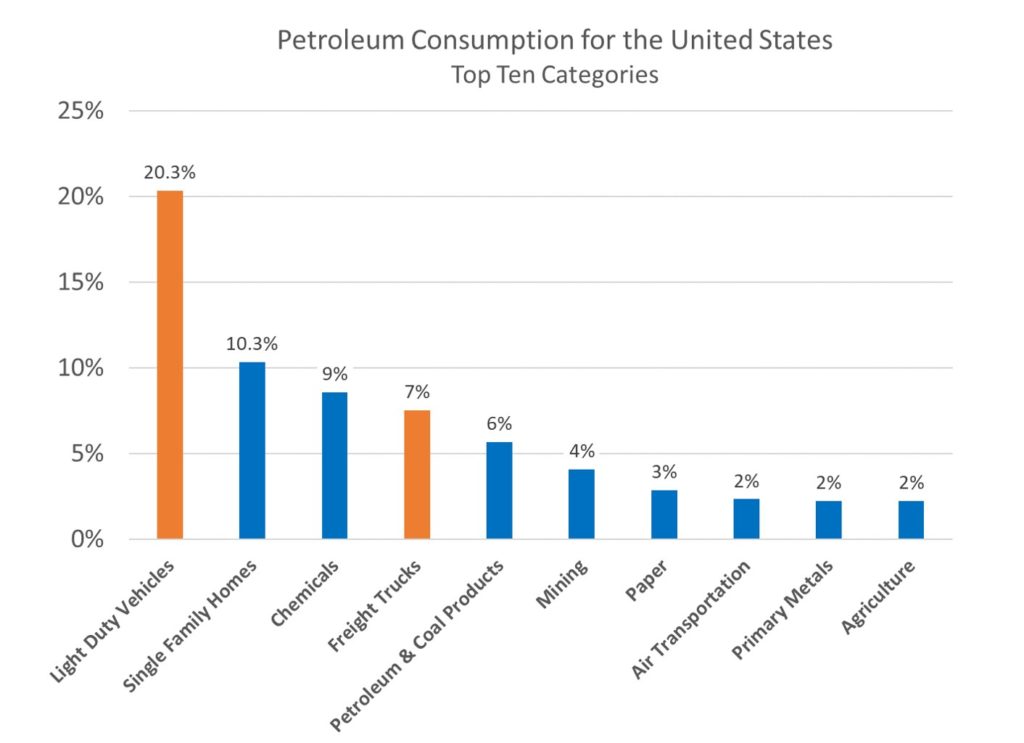
Using the same data set, I created a chart to break out the top ten categories for petroleum consumption for the United States.
The category Light-Duty Vehicles (cars, light trucks) is the largest consumer at 20% and is more than the sum of the next two categories – Single-Family Homes (10%) and Chemicals (9%).
When Light-Duty Vehicles at 20% are combined with Freight Trucks (think eighteen-wheelers) at 7%, they make up 27% of the country’s total consumption, making the Transportation sector the thirstiest. The most effective way to reduce petroleum consumption is to replace vehicles powered by internal combustion engines with electric vehicles (EVs). But there’s a catch.
As internal combustion engines diminish and EVs come online, petroleum consumption will drop and will help the planet. But, as EVs come online the demand for electricity will increase, making it even more important to replace coal and natural gas with zero-carbon sources of electricity: nuclear, hydro, wind and solar.
To save the planet, here’s what you can do. Vote for political candidates who will end federal subsidies for coal and natural gas. That single change will accelerate the adoption of wind and solar, as it will increase the existing cost advantage of wind and solar. And if that freed-up money can be reallocated to federally-funded R&D to improve the controllability of electrical grids, the change will come even sooner.
And at the state and local level, you can vote for candidates that want to make it easier for wind and solar projects to be funded.
And, lastly, you can buy an EV. You will see a much larger selection of new electric vehicles over the next year and the driving range continues to improve. Over the next year, most new EV models will be high performance and high cost, lower-cost EVs should follow soon after.
Image credit – NASA Goodard Flight Center
How is your electricity made?
 How is your electricity made? Which source produces the most electricity? How much is made from zero-carbon sources? How much is made from renewable sources?
How is your electricity made? Which source produces the most electricity? How much is made from zero-carbon sources? How much is made from renewable sources?
In 2017, Otherlab was contracted by the Advanced Research Project Agency of the Department of Energy (ARPA-e) to review all available energy data sources and create an ultra-high resolution picture of the U.S. energy economy. The purpose was to identify research priorities and to model scenarios for new energy technologies and policies. This work leveraged many decades of effort by the U.S. Energy Information Agency (PDF) and Lawrence Livermore National Lab analyzing the U.S. energy economy and providing annual snapshots in a Sankey Flow Diagram format. The Otherlab “Super Sankey” tool is available at www.departmentof.energy
Here’s a link to Otherlab’s original post on the project.
The Sankey Flow diagram format can be difficult at first, so I created a simple chart to break down the electricity sources for the United States.
As you can see, we have a long way to go to replace coal and natural gas, the two most troublesome sources for the planet. Together, coal and gas are responsible for 63% of the country’s electricity. The next largest source is nuclear at 22%. Nuclear is a carbon-free source of electricity, but it’s not renewable and it produces waste that must be stored for a long time in secure vaults. Nuclear is often considered a good solution to produce carbon-free electricity (at least while renewable sources come online), but it’s a politically charged technology due to the perceived danger of catastrophic failure of nuclear powerplants.
The largest renewable source of electricity is hydro at 6% and wind is next at 5%. We hear a lot about solar, but it produces a small fraction of our electricity. And we don’t hear much about geothermal which is about half the size of solar.
These numbers may differ a bit from those calculated from other data sources, but the picture is clear. We’ve got a long way to go to displace coal and natural gas. But the cost of renewable sources is now less than coal and natural gas. You’ll soon see more coal plants closing and reduced sales of natural gas power turbine generators.
If we are to do one thing to accelerate the transition to renewable sources of electricity, we should end subsidies paid to coal and natural gas industries and use the freed-up money to create the next-generation technologies that help the grid accept more renewable sources of electricity.
Image credit – Andreas Øverland
Whatever your situation, be thankful for it.
 If you’re thankful for the success you’ve had, you’re in for a letdown because your success will be short-lived. And don’t take it personally – the Universe knows regression to the mean is real and it will bring you to your knees whether you believe it or not. Like with all things, success is impermanent.
If you’re thankful for the success you’ve had, you’re in for a letdown because your success will be short-lived. And don’t take it personally – the Universe knows regression to the mean is real and it will bring you to your knees whether you believe it or not. Like with all things, success is impermanent.
Your success has a half-life. Sure, your success has been good. You’ve made money; your brand has prospered, and everyone is happy. But, don’t get too comfortable because it’s going away. Your recipe will run out of gas as your competition targets your success and figures out how to do it better. But don’t blame your competitors’ hard work. Blame yourself and your success. It’s pretty clear your success has blocked you from doing things differently. The real problem isn’t your competitors’ success; the real problem is your success. Your success has blocked you from trying something new. As the thinking goes – if it ain’t broke, don’t fix it. But, if it ain’t broke now, it will be broken soon.
If you’re sad (unthankful) because of the failure you’ve experienced, you’re in for a burst of goodness because your failure will be short-lived. And don’t feel special – the Universe knows regression to the mean is real and it will bring you success if you believe you’re worthy of it. Like with all things, failure is impermanent.
Your failure has a half-life. Sure, your failure has been bad. You’ve not made money; your brand has suffered; and everyone is unhappy. But, don’t hold onto your discomfort because it’s going away. Because your recipe hasn’t worked, you’ll target your competitors’ success and try a new recipe. It’s pretty clear your lack of success caused you to try a new recipe. And because you tried something new, you figured out how to do it better. But Don’t give credit to your competitors. Give credit to yourselves for trying something new. The real root cause isn’t your competitors’ success; the real forcing function is your lack of success. Your lack of success has opened up your thinking and enabled you to try something new. As the thinking goes – if it didn’t work last time, do something different. And that’s just what you did.
Don’t be thankful for your success; be thankful you have smart people who want to make a difference. And don’t be unthankful for your failure; be thankful you have smart people who want to make a difference.
As a leader in a successful company, what will you do to support people who want to make a difference? As a leader, you must protect their new ideas from the army of people that want to regurgitate what was done last time. Because of your success, their new ideas will be taken out at the knees. And what will you do? Will you roll over and kowtow to un-thinkers? Or, will you take the bullets and advocate for ideas that violate your long-in-the-tooth, geriatric recipe that can no longer deliver what it used to?
And as a leader in a yet-to-be successful company, what will you do to support people who want to make a difference? As a leader, you must protect their new ideas from the army of people that have no idea what to do next. Because of your failure, their new ideas will be met with negativity and derision. And what will you do? Will you give in to the naysayers? Or, will you take the bullets and advocate for ideas that transcend your unsuccessful recipe?
Be thankful for your success, but don’t let it limit you from trying something new. And be thankful for your failure, and use it to power your new ideas.
Whatever your situation, don’t dismiss it. Whatever your situation, learn from it. And whatever your situation, be thankful for it.
Image credit — Irudayam
All-or-Nothing vs. One-in-a-Row
 All-or-nothing thinking is exciting – we’ll launch a whole new product family all at once and take the market by storm! But it’s also dangerous – if we have one small hiccup, “all” turns into “nothing” in a heartbeat. When you take an all-or-nothing approach, it’s likely you’ll have far too little “all” and far too much “nothing”.
All-or-nothing thinking is exciting – we’ll launch a whole new product family all at once and take the market by storm! But it’s also dangerous – if we have one small hiccup, “all” turns into “nothing” in a heartbeat. When you take an all-or-nothing approach, it’s likely you’ll have far too little “all” and far too much “nothing”.
Instead of trying to realize the perfection of “all”, it’s far better to turn nothing into something. Here’s the math for an all-or-nothing launch of product family launch consisting of four products, where each product will create $1 million in revenue and the probability of launching each product is 0.5 (or 50%).
1 product x $1 million x 0.5 = $500K
2 products x $1 million x 0.5 x 0.5 = $500K
3 products x $1 million x 0.5 x 0.5 x 0.5 = $375K
4 products x $1 million x 0.5 x 0.5 x 0.5 x 0.5 = $250K
In the all-or-nothing scheme, the launch of each product is contingent on all the others. And if the probability of each launch is 0.5, the launch of the whole product family is like a chain of four links, where each link has a 50% chance of breaking. When a single link of a chain breaks, there’s no chain. And it’s the same with an all-or-nothing launch – if a single product isn’t ready for launch, there are no product launches.
But the math is worse than that. Assume there’s new technology in all the products and there are five new failure modes that must be overcome. With all-or-nothing, if a single failure mode of a single product is a problem, there are no launches.
But the math is even more deadly than that. If there are four use models (customer segments that use the product differently) and only one of those use models creates a problem with one of the twenty failure modes (five failure modes times four products) there can be no launches. In that way, if 25% of the customers have one problem with a single failure mode, there are can be no launches. Taken to an extreme, if one customer has one problem with one product, there can be no launches.
The problem with all-or-nothing is there’s no partial credit – you either launch four products or you launch none. Instead of all-or-nothing, think “secure the launch”. What must we do to secure the launch of a single product? And once that one’s launched, the money starts to flow. And once we launch the first one, what must we do to secure the launch the second? (More money flows.) And, once we launch the third one…. you get the picture. Don’t try to launch four at once, launch a single product four times in a row. Instead of all-or-nothing, think one-in-a-row, where revenue is achieved after each launch of a single launch.
And there’s another benefit to launching one at a time. The second launch is informed by learning from the first launch. And the third is informed by the first two. With one-in-a-row, the team gets smarter and each launch gets better.
Where all-or-nothing is glamorous, one-in-a-row is achievable. Where all-or-nothing is exciting, one-in-row is achievable. And where all-or-nothing is highly improbable, one-in-a-row is highly profitable.
Image credit – Mel
Companies, Acquisitions, Startups, and Hurricanes
If you run a company, the most important thing you can control is how you allocate your resources. You can’t control how the people in your company will respond to input, but you can choose the projects they work on. You can’t control which features and functions your customers will like, but you can choose which features and functions become part of the next product. And you can’t control if a new technology will work, but you can choose the design space to investigate. The open question – How to choose in a way that increases your probability of success?
If you want to buy a company, the most important thing you can control is how you allocate your resources. In this case, the resources are your hard-earned money and your choice is which company to buy. The open question – How to choose in a way that increases your probability of success?
If you want to invest in a startup company, the most important thing you can control is how you allocate your resources. This case is the same as the previous one – your money is the resource and the company you choose defines how you allocate your resources. This one is a little different in that the uncertainty is greater, but so is the potential reward. Again, the same open question – How to choose in a way that increases your probability of success?
Taking a step back, the three scenarios can be generalized into a category called a “system.” And the question becomes – how to understand the system in a way that improves resource allocation and increases your probability of success?
These people systems aren’t predictable in an if-A-then-B way. But they do have personalities or dispositions. They’ve got characteristics similar to hurricanes. A hurricane’s exact path cannot be forecasted, the meteorologist can use history and environmental conditions to broadly define regions where the probability of danger is higher. The meteorologist continually monitors the current state of the hurricane (the system as it is) and tracks its position over time to get an idea of its trajectory (a system’s momentum). The key to understanding where the hurricane could go next: where it is right now (current state), how it got there (how it has behaved over time), and how have other hurricanes tracked under similar conditions (its disposition). And it’s the same for systems.
To improve your understanding of how your system may respond, understand it as it is. Define the elements and how those elements interact. Then, work backward in time to understand previous generations of the system. Which elements were improved? Which ones were added? Then, like the meteorologist, start at the system’s genesis and move forward to the present to understand its path. Use the knowledge of its path and the knowledge of systems (it’s important to be the one that improves the immature elements of the system and systems follow S-curves until the S-curve flattens) to broadly define regions where the probability of success is higher.
These methods won’t guarantee success. But, they will help you choose projects, choose acquisitions, choose technologies, and choose startups in a way that increases your probability of success.
Image credit — Alexander Gerst
When Problems Are Bigger Than They Seem
If words and actions are different, believe the actions.
If the words change over time, don’t put stock in the person delivering them.
If a good friend doesn’t trust someone, neither should you.
If the people above you don’t hold themselves accountable, yet they try to hold you accountable, shame on them.
If people are afraid to report injustices, it’s just a matter of time before the best people leave.
If actions are consistently different than the published values, it’s likely the values should be up-revved.
If you don’t trust your leader, respect your instincts.
If people are bored and their boredom is ignored, expect the company to death spiral into the ground.
If behaviors are different than the culture, the culture isn’t the culture.
If all the people in a group apply for positions outside the group, the group has a problem.
When actions seen by your eyes are different than the rhetoric force-fed into your ears, believe your eyes.
If you think your emotional wellbeing is in jeopardy, it is.
If to preserve your mental health you must hunker down with a trusted friend, find a new place to work.
If people are afraid to report injustices, company leadership has failed.
If the real problems aren’t discussed because they’re too icky, there’s a bigger problem.
If everyone in the group applies for positions outside the group and HR doesn’t intervene, the group isn’t the problem.
And to counter all this nonsense:
If someone needs help, help them.
If someone helps you, thank them.
If someone does a good job, tell them.
Rinse, and repeat.
Now that you know your product is bad for the environment, what will you do?
 If your products were bad for the environment, what would you do?
If your products were bad for the environment, what would you do?
If your best products were the worst for the environment, what would you do?
If you knew your products hurt the people that use them, what would you do?
If you knew your sales would be reduced if you told your customers that your products were bad for their health, what would you do?
If you knew a competitive technology was fundamentally less harmful to the environment, what would you do?
If you knew that competitive technology did not hurt the people that use it, what would you do?
If you knew that competitive technology was taking market share from you, what would you do?
If you knew that competitive technology was improving faster than yours, what would you do?
If you knew how to redesign your product to make it better for the environment, but that redesign would reduce the product’s performance in other areas, what would you do?
If that same redesign effort generated patented technology, what would you do?
So, what will you do?
Image credit — Shane Gorski




 Mike Shipulski
Mike Shipulski