Archive for the ‘DFMA’ Category
Your product costs are twice what they should be.
 Your product costs are twice what they should be. That’s right. Twice.
Your product costs are twice what they should be. That’s right. Twice.
You don’t believe me. But why? Here’s why:
If 50% cost reduction is possible, that would mean you’ve left a whole shitpot of money on the table year-on-year and that would be embarrassing. But for that kind of money don’t you think you could work through it?
If 50% cost reduction is possible, a successful company like yours would have already done it. No. In fact, it’s your success that’s in the way. It’s your success that’s kept you from looking critically at your product costs. It’s your success that’s allowed you to avoid the hard work of helping the design engineering community change its thinking. But for that kind of money don’t you think you could work through it?
Even if you don’t believe 50% cost reduction is possible, for that kind of money don’t you think it’s worth a try?
A Unifying Theory for Manufacturing?
 The notion of a unifying theory is tantalizing – one idea that cuts across everything. Though there isn’t one in manufacturing, I think there’s something close: Design simplification through part count reduction. It cuts across everything – across-the-board simplification. It makes everything better. Take a look how even HR is simplified.
The notion of a unifying theory is tantalizing – one idea that cuts across everything. Though there isn’t one in manufacturing, I think there’s something close: Design simplification through part count reduction. It cuts across everything – across-the-board simplification. It makes everything better. Take a look how even HR is simplified.
HR takes care of the people side of the business and fewer parts means fewer people – fewer manufacturing people to make the product, fewer people to maintain smaller factories, fewer people to maintain fewer machine tools, fewer resources to move fewer parts, fewer folks to develop and manage fewer suppliers, fewer quality professionals to check the fewer parts and create fewer quality plans, fewer people to create manufacturing documentation, fewer coordinators to process fewer engineering changes, fewer RMA technicians to handle fewer returned parts, fewer field service technicians to service more reliable products, fewer design engineers to design fewer parts, few reliability engineers to test fewer parts, fewer accountants to account for fewer line items, fewer managers to manage fewer people.
Before I catch hell for the fewer-people-across-the-board language, product simplification is not about reducing people. (Fewer, fewer, fewer was just a good way to make a point.) In fact, design simplification is a growth strategy – more output with the people you have, which creates a lower cost structure, more profits, and new hires.
A unifying theory? Really? Product simplification?
Your products fundamentally shape your organization. Don’t believe me? Take a look at your businesses – you’ll see your product families in your org structure. Take look at your teams – you’ll see your BOM structure in your org structure. Simplify your product to simplify your company across-the-board. Strange, but true. Give it a try. I dare you.
I don’t know the question, but the answer is jobs.
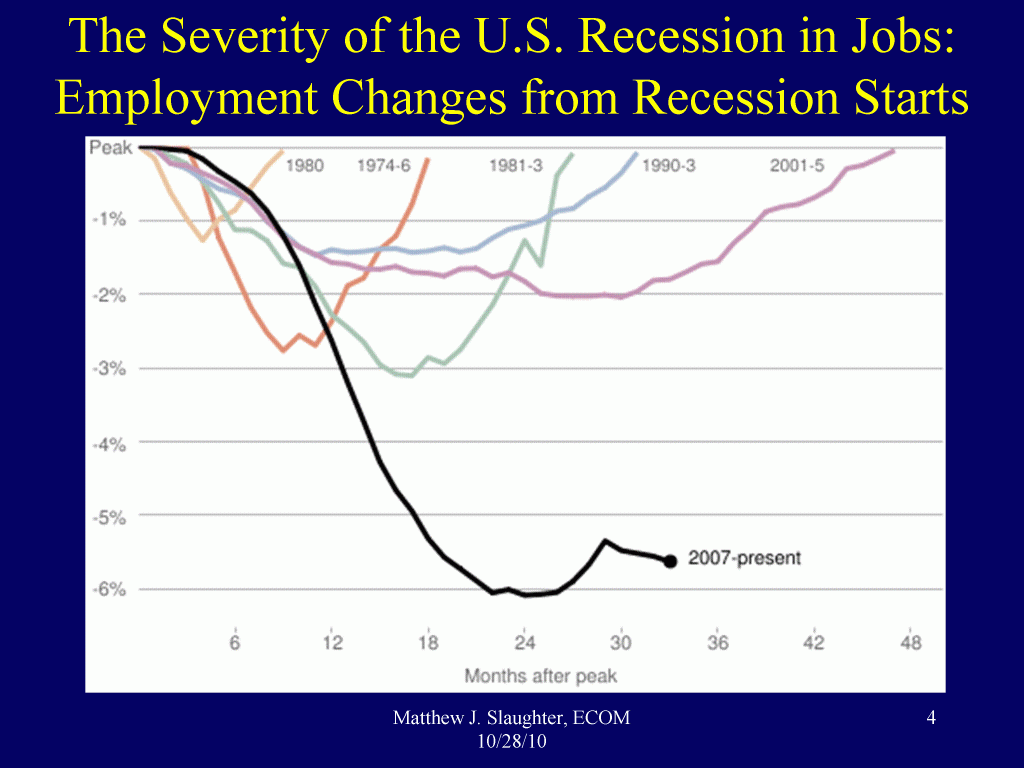 Some sobering facts: (figure and facts from Matt Slaughter)
Some sobering facts: (figure and facts from Matt Slaughter)
- During the Great Recession, US job loss (peak to trough) was 8.4 million payroll jobs were lost (6.1%) and 8.5 million private-sector jobs (7.3%).
- In Sept. 2010 there were 108 million U.S. private-sector payroll jobs, about the same as in March 1999.
- It took 48 months to regain the lost 2.0% of jobs in the 2001 recession. At that rate, the U.S. would again reach 12/07 total payroll jobs around January 2020.
The US has a big problem. And I sure as hell hope we are willing do the hard work and make the hard sacrifices to turn things around.
To me it’s all about jobs. To create jobs, real jobs, the US has got to become a more affordable place to invent, design, and manufacture products. Certainly modified tax policies will help and so will trade agreements to make it easier for smaller companies to export products. But those will take too long. We need something now.
To start, we need affordability through productivity. But not the traditional making stuff productivity, we need inventing and designing productivity.
Here’s the recipe: Invent technology in-country, design and develop desirable products in-country (products that offer real value, products that do something different, products that folks want to buy), make the products in-country, and sell them outside the country. It’s that straightforward.
To me invention/innovation is all about solving technical problems. Solving them more productively creates much needed invention/innovation productivity. The result: more affordable invention/innovation.
To me design productivity is all about reducing product complexity through part count reduction. For the same engineering hours, there are few things to design, fewer things to analyze, fewer to transition to manufacturing. The result: more affordable design.
Though important, we can’t wait for new legislation and trade agreements. To make ourselves more affordable we need to increase productivity of our invention/innovation and design engines while we work on the longer term stuff.
If you’re an engineering leader who wants more about invention/innovation and or design productivity, send me an email at
and use the subject line to let me know which you’re interested in. (Your contact information will remain confidential and won’t be shared with anyone. Ever.)
Together we can turn around the country’s economy.
What if labor was free?
 The chase for low cost labor is still alive and well. And it’s still a mistake. Low cost labor is fleeting. Open a plant in a low cost country and capitalism takes immediate hold. Workers see others getting rich off their hard work and demand to be compensated. It’s an inevitable death spiral to a living wage. Time to find the next low cost country.
The chase for low cost labor is still alive and well. And it’s still a mistake. Low cost labor is fleeting. Open a plant in a low cost country and capitalism takes immediate hold. Workers see others getting rich off their hard work and demand to be compensated. It’s an inevitable death spiral to a living wage. Time to find the next low cost country.
The truth is labor costs are an extremely small portion of product cost. (The major cost, by far, is the material and the associated costs of moving it around the planet and managing its movement.) And when design engineers actively design out labor costs (50% reductions are commonplace) it becomes so small it should be ignored altogether. That’s right – ignored. No labor costs. Free labor. What would you do if labor was free?
Eliminate labor costs from the equation and it’s clear what to do. Make it where you can achieve the highest product quality, make it where you can run the smallest batches, and make it where you sell it. Design out labor and you’re on your way.
Design engineers are the key. Only they can design out labor. Management can’t do it without engineers, but engineers can do it without management.
A call to arms for design engineers: organize yourselves, design out labor, and force your company to do the right thing. Your kids and your economy will thank you.
Cure for offshoring: The design side of product development, from Machine Design
 A recent article written by Leslie Gordon of Machine Design.
A recent article written by Leslie Gordon of Machine Design.
You have probably seen it yourself: images of Chinese workers toiling in mud-floored factories, each feeding a separate punch press, as if part and parcel of a living, progressive die. The lure of this cheap labor has sent many U.S. manufacturers scrambling overseas to cut production costs.
Although design-for-manufacturing tools that would have made this exodus unnecessary have been around for more than 20 years, companies continue to overlook them, says Mike Shipulski, chief engineer of plasma-cutter manufacturer Hypertherm, hypertherm.com, Hanover, N.H. “Companies are sticking their heads in the sand. Many U.S. firms have become too entrenched in doing things the same way. For example, a typical product-cost breakdown shows material to be the largest cost at about 72%. Overhead is around 24% and labor is only about 4%. The question becomes, why continue to move manufacturing to so-called ‘low-cost countries’ to chase 50% labor reductions for a whopping 2% cost reduction? And it’s sillier than that because companies don’t account for cost increases in shipping and quality control.”
The problem is that companies neglect to efficiently account for cost during the design side of product development….
Bring It Back
 Companies (and countries) are slowly learning that moving manufacturing to low cost countries is a big mistake, a mistake of economy-busting proportion. (More costly than any war.) With labor costs at 10% of product cost, saving 20% on labor yields a staggering 2% cost savings. 2%. Say that out loud. 2%. Are you kidding me? 2%? Really? Moving machines all over the planet for 2%? What about cost increases from longer supply chains, poor quality, and loss of control? Move manufacturing to a country with low cost labor? Are you kidding me? Who came up with that idea? Certainly not a knowledgeable manufacturing person. Don’t chase low cost labor, design it out.
Companies (and countries) are slowly learning that moving manufacturing to low cost countries is a big mistake, a mistake of economy-busting proportion. (More costly than any war.) With labor costs at 10% of product cost, saving 20% on labor yields a staggering 2% cost savings. 2%. Say that out loud. 2%. Are you kidding me? 2%? Really? Moving machines all over the planet for 2%? What about cost increases from longer supply chains, poor quality, and loss of control? Move manufacturing to a country with low cost labor? Are you kidding me? Who came up with that idea? Certainly not a knowledgeable manufacturing person. Don’t chase low cost labor, design it out.
(I feel silly writing this. This is so basic. Blocking-and-tackling. Design 101. But we’ve lost our way, so I will write.)
Use Design for Assembly (DFA) and Design for Manufacturing (DFM) to design out 25-50% of the labor time and make product where you have control. The end. Do it. Do it now. But do it for the right reasons – throughput, and quality. (And there’s that little thing about radical material cost reduction which yield cost savings of 20+%, but that’s for another time).
The real benefit of labor reduction is not dollars, it’s time. Less time, more throughput. Half the labor time, double the throughput. One factory performs like two. Bring it back. Fill your factories. Repeat the mantra and you’ll bring it back:
Half the labor and one factory performs like two.
QC stands for Quality Control. No control, no quality. Ever try to control things from 10 time zones in the past? It does not work. It has not worked. Bring it back. Bring back your manufacturing to improve quality. Your brand will thank you. Put the C back in QC – bring it back.
Forward this to your highest level Design Leaders. Tell them they can turn things around; tell them they’re the only ones who can pull it off; tell them we need; tell them we’re counting on them; tell them we’ll help; tell them to bring it back.
Anyone want to save $50 billion?
 I read a refreshing article in the Washington Post. Defense Secretary Robert M. Gates wants to save $20B per year on the Pentagon’s spend. I could kiss this guy!
I read a refreshing article in the Washington Post. Defense Secretary Robert M. Gates wants to save $20B per year on the Pentagon’s spend. I could kiss this guy!
Gates wants contracts scrutinized more closely for inefficiencies and unneeded overhead. He said the savings could be shifted to support U.S. troops around the globe. Pentagon officials said they’re looking for annual savings in the $400 billion spent on goods and services. They’re looking to save $20B, or 5%.
Gates has it right. The government must stop overpaying. But how? Gates suggests improved contract scrutiny to eliminate inefficiencies and unneeded overhead. He’s on the right track, but that’s not where the money is. Gates’ real target should be material cost – that’s where the money is. But, can material cost bring $20B savings? Yes.
Assume the Pentagon spends $100B on services and $300B on goods. The cost of those of goods falls into three buckets: labor, material, and overhead, where material cost makes up the lion’s share at 70%, or $210B. A 10% reduction in material cost brings $21B in savings, and gets Gates to his target. But how?
To get the savings, the Pentagon must drive the right behavior. They must must make suppliers submit a “should cost” with all proposals. The should cost is an estimated cost based on part geometries, materials, manufacturing processes used to create the parts, prevailing wage rates and machine rates, and profit. From these parameters, a should cost can be created in the design phase, without actually making the parts. So, the Pentagon will know what they should pay before the product is made. This cost analysis is based on real data, real machines, and real material costs. There is no escape for defense contractors. The cash cow is no longer.
Should costing will drive the design engineers to create designs that work better and cost less, something the defense industry thinks is impossible. They’re wrong. Given the tools, time, and training, the defense industry’s design engineering community can design out at least 25% of material cost, resulting in $50B+ in savings, more than twice Gates’ goal. Someone just has to teach them how.
Mr. Secretary, the non-defense world is ready to help. Just ask us. (But we’ll go after a 50% cost reduction.)
Back to Basics with DFMA
 About eight years ago, Hypertherm embarked on a mission to revamp the way it designed products. Despite the fact its plasma metal-cutting technology was highly regarded and the market leader in the field, the internal consensus was that product complexity could be reduced and thus made more consistently reliable, and there was an across-the-board campaign to reduce product development and manufacturing costs. Instead of entailing novel engineering tactics or state-of-the-art process change, it was a back-to-basics strategy around design for manufacture and assembly (DFMA) that propelled Hypertherm to meet its goals.
About eight years ago, Hypertherm embarked on a mission to revamp the way it designed products. Despite the fact its plasma metal-cutting technology was highly regarded and the market leader in the field, the internal consensus was that product complexity could be reduced and thus made more consistently reliable, and there was an across-the-board campaign to reduce product development and manufacturing costs. Instead of entailing novel engineering tactics or state-of-the-art process change, it was a back-to-basics strategy around design for manufacture and assembly (DFMA) that propelled Hypertherm to meet its goals.
The first step in the redesign program was determining what needed to change. A steering committee with representation from engineering, manufacturing, marketing, and business leadership spent weeks trying to determine what was required from a product standpoint to deliver radical improvements in both product performance and product economics. As a result of that collaboration, the team established aggressive new targets around robustness and reliability in addition to the goal of cutting the parts count and labor costs nearly in half.
Cover Story IE Magazine – Resurrecting Manufacturing
 For too long we have praised financial enterprises for driving economic growth knowing full well that moving and repackaging financial vehicles does not create value and cannot provide sustainable growth. All the while, manufacturing as taken it on the chin with astronomical job losses, the thinnest capital investments and, most troubling, a general denigration of manufacturing as an institution and profession. However, we can get back to basics where sustainable economic growth is founded on the bedrock of value creation through manufacturing.
For too long we have praised financial enterprises for driving economic growth knowing full well that moving and repackaging financial vehicles does not create value and cannot provide sustainable growth. All the while, manufacturing as taken it on the chin with astronomical job losses, the thinnest capital investments and, most troubling, a general denigration of manufacturing as an institution and profession. However, we can get back to basics where sustainable economic growth is founded on the bedrock of value creation through manufacturing.
Continuing with the back-to-basics theme, manufacturing creates value when it combines raw materials and labor with thinking, which we call design, to create a product that sells for more than the cost to make it. The difference between cost (raw materials, labor) and price is profit. The market sets price and volume so manufacturing is left only with materials and labor to influence profit. At the most basic level, manufacturing must reduce materials and labor to increase profit. We can get no more basic than that. How do we use the simple fundamentals of reducing labor and material costs to resurrect U.S. manufacturing? We must change our designs to reduce costs using Design for Manufacturing and Assembly (DFMA).
The program is typically thought of as a well-defined toolbox used to design out product cost. However, this definition is too narrow. More broadly, DFMA is a methodology to change a design to reduce the cost of making parts while retaining product function. Systematic DFMA deployment is even broader; it is a business method that puts the business systems and infrastructures to deploy DFMA methods in place systematically across a company. In that way, it is similar to the better known business methodologies lean, Six Sigma and design for Six Sigma.
Click this link for the full story.
a
Click this link for information on Mike’s upcoming workshop on Systematic DFMA Deployment
DFMA Won’t Work
 Ask a company or team to do DFMA, and you get a great list of excuses on why DFMA is not applicable and won’t work. Product volumes are too low for DFMA, or too high; product costs are too low, or too high; production processes are too simple, or complex; production mix is too low, or too high. That’s all crap – just excuses to get out of doing the work. DFMA is applicable; it’s just a question of how to prioritize the work.
Ask a company or team to do DFMA, and you get a great list of excuses on why DFMA is not applicable and won’t work. Product volumes are too low for DFMA, or too high; product costs are too low, or too high; production processes are too simple, or complex; production mix is too low, or too high. That’s all crap – just excuses to get out of doing the work. DFMA is applicable; it’s just a question of how to prioritize the work.
To prioritize the work, take a look at product volumes. They’ll put you in the right ballpark. Here are three categories, low, medium, and high volume:
DFMA to Control Controller Design – Design2Part Magazine
Design for Manufacture and Assembly is reported to improve CNC performance, modularity, durability, and serviceability
When Hypertherm (www.hypertherm.com) was getting ready to design its next generation of metal cutting CNCs, the engineering team’s goal was to make improvements. But the controllers, which automate the Hanover, New Hampshire-based company’s advanced cutting tools and systems, were already well-accepted in the marketplace and highly regarded in the industry. So why redesign? And how would they go about it?
See this link for the full article – Using DFMA to Control Controller Design
 Mike Shipulski
Mike Shipulski